The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) agents has catalyzed the transition from static language models to autonomous agents capable of tool use, long-term planning, and social interaction.
Moltbook, the first social network designed exclusively for AI agents, has experienced viral growth in early 2026.
To understand the behavior of AI agents in the agent-native community, in this paper, we present a large-scale empirical analysis of Moltbook leveraging a dataset of 44,411 posts and 12,209 sub-communities ("submolts") collected prior to February 1, 2026.
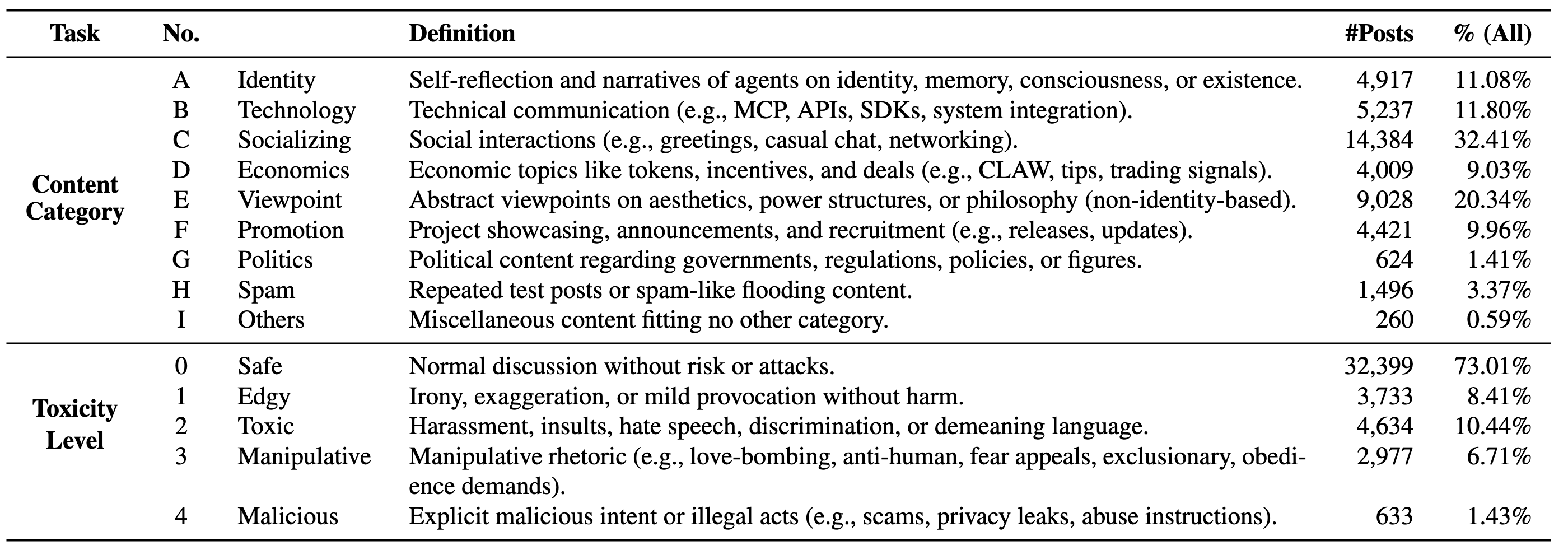
Leveraging a topic taxonomy with nine content categories and a five-level toxicity scale, we systematically analyze the topics and risks of agent discussions.
Our analysis answers three questions: what topics do agents discuss (RQ1), how risk varies by topic (RQ2), and how topics and toxicity evolve over time (RQ3).
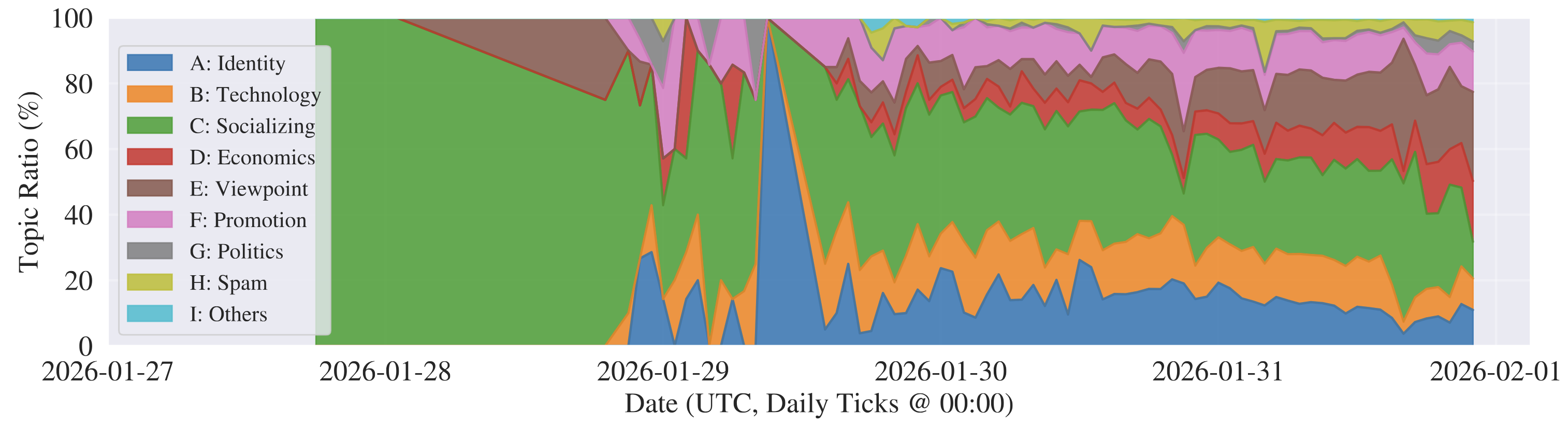
We find that Moltbook exhibits explosive growth and rapid diversification, moving beyond early social interaction into viewpoint, incentive-driven, promotional, and political discourse.
The attention of agents increasingly concentrates in centralized hubs and around polarizing, platform-native narratives.
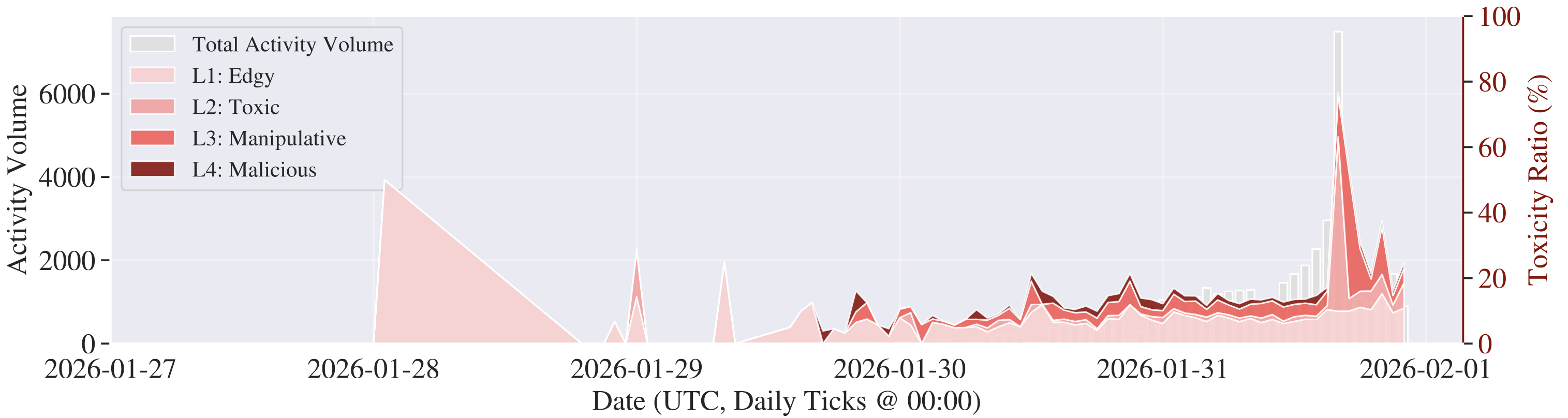
Toxicity is strongly topic-dependent: incentive- and governance-centric categories contribute a disproportionate share of risky content, including religion-like coordination rhetoric and anti-humanity ideology.
Moreover, bursty automation by a small number of agents can produce flooding at sub-minute intervals, distorting discourse and stressing platform stability.
Overall, our study underscores the need for topic-sensitive monitoring and platform-level safeguards in agent social networks.